Title: When Will Home Prices Go Down? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Market Trends and Predictions
With record-breaking home prices and intense competition in the housing market, many prospective buyers wonder: “When will home prices go down?” Predicting housing market trends is challenging, especially with variables like interest rates, inflation, and supply and demand. This guide explores the factors influencing home prices, expert predictions, and what potential homebuyers should consider as they plan their next move.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Trends in Home Prices
- Factors That Influence Home Prices
- 3.1 Interest Rates and Mortgage Rates
- 3.2 Inflation and the Cost of Living
- 3.3 Supply and Demand in the Housing Market
- Regional Differences in Housing Prices
- Expert Predictions for Home Prices in the Coming Years
- Is Waiting for a Price Drop the Best Strategy?
- What Buyers Can Do Now: Preparation Strategies
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
For many, buying a home feels increasingly out of reach as home prices continue to rise. Prospective buyers are left wondering if, or when, the market will cool down and prices will become more affordable. This article dives into historical data, economic factors, and expert insights to help answer the question, “When will home prices go down?”
2. Historical Trends in Home Prices
Examining the history of home prices offers valuable context for current trends. Housing prices tend to follow cycles of growth, stability, and occasional declines. Here’s a look at historical price changes in the U.S. over the past few decades:
| Decade | Average Home Price Increase | Key Events Influencing Prices |
|---|---|---|
| 1980s | Moderate increase | High inflation, but economic growth |
| 1990s | Stable growth | Tech boom, increased demand |
| 2000s | Major rise and crash | Housing bubble and 2008 financial crisis |
| 2010s | Steady recovery and growth | Low interest rates, increased urbanization |
| 2020s | Rapid rise | Pandemic, supply shortages, low mortgage rates |
Key Takeaways:
- Cycles of Growth and Decline: Home prices typically increase over time but can experience declines during economic downturns.
- The 2008 Housing Crisis: One of the most significant drops in modern history, with prices taking years to recover.
- Pandemic Impact: The COVID-19 pandemic caused an unprecedented surge in demand and low mortgage rates, pushing prices to record highs.
3. Factors That Influence Home Prices
Various factors impact housing prices, and understanding these can provide insight into when and why prices might decrease.
3.1 Interest Rates and Mortgage Rates
Mortgage interest rates have a direct impact on home affordability:
| Interest Rate Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Low Rates | Increase demand as monthly payments are more affordable, pushing prices up. |
| High Rates | Decrease demand, as higher payments reduce affordability, potentially slowing price growth. |
3.2 Inflation and the Cost of Living
Inflation increases the cost of building materials, labor, and land, contributing to higher home prices. If inflation rates stabilize, it could slow the rate of price increases, but a significant drop is unlikely without broader economic adjustments.
3.3 Supply and Demand in the Housing Market
The balance between housing supply and demand heavily influences prices:
| Factor | Impact on Prices |
|---|---|
| Low Supply | Drives prices up as buyers compete for limited homes. |
| High Demand | Increases prices, particularly in high-demand areas like cities and suburbs. |
| New Construction Trends | Increased construction could help stabilize prices if demand is met. |
| Zoning and Regulations | Restrictive zoning can limit new construction, exacerbating supply shortages. |
4. Regional Differences in Housing Prices
Not all areas experience housing market trends in the same way. Prices in urban centers, high-demand regions, and tech hubs tend to rise faster than in rural or less-populated areas.
| Region Type | Price Trends |
|---|---|
| Urban Centers | High demand and limited space lead to faster price increases, especially in tech-driven cities. |
| Suburban Areas | Growing popularity post-pandemic has led to rising prices in many suburban regions. |
| Rural Areas | Prices tend to rise more slowly due to lower demand and greater availability of land. |
Example:
In 2021, prices in cities like San Francisco and New York were high, but rural areas in states like Idaho and Montana also saw spikes due to remote work trends.
5. Expert Predictions for Home Prices in the Coming Years
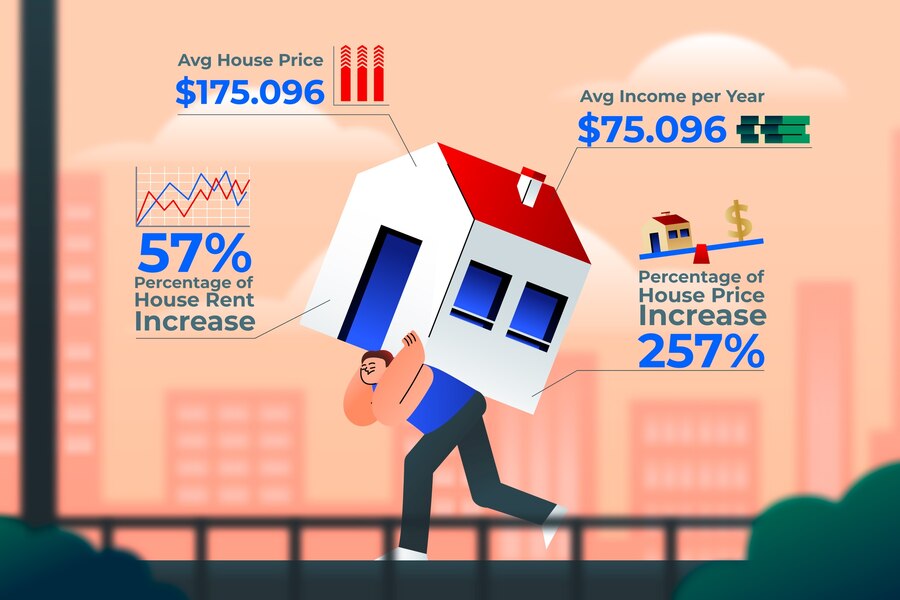
Here’s what some experts forecast for home prices:
| Prediction | Reasoning |
|---|---|
| Moderate Growth | Some economists predict slower growth due to rising interest rates and potential economic cooling. |
| Regional Declines | High-cost urban areas may see slight price drops as buyers move to more affordable locations. |
| Slight Price Drops | Certain areas may experience modest declines if construction increases and demand stabilizes. |
Many economists anticipate that while price growth may slow, significant price drops nationwide are unlikely without a major economic shift. Some areas, especially high-priced markets, could see small reductions, but a widespread decrease is not guaranteed.
6. Is Waiting for a Price Drop the Best Strategy?
While waiting for prices to fall may seem prudent, it’s a strategy that comes with risks. For many prospective buyers, waiting can mean missing out on potential equity and appreciation, while the costs of renting continue to increase. Additionally, if interest rates continue to rise, it could offset any potential savings from a small price reduction.
Factors to Consider When Deciding:
- Interest Rates: If rates rise while you wait, buying later may still be more expensive, even with a slight drop in home prices.
- Local Market Conditions: In high-demand areas, prices may not decrease as much or as quickly.
- Financial Stability: Assess your own financial situation, savings, and future plans. If you’re financially ready and plan to stay in the home long-term, buying now may still be wise.
7. What Buyers Can Do Now: Preparation Strategies
If you’re planning to buy a home but aren’t sure when to jump in, here are some proactive steps to take.
| Preparation Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Build Your Savings | Aim to save 20% for a down payment to avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI) and lower costs. |
| Improve Your Credit Score | A higher credit score will help you secure a lower interest rate, saving money over time. |
| Reduce Debt | Lower your debt-to-income ratio to improve mortgage approval chances and affordability. |
| Explore Different Markets | Consider smaller cities or suburban areas that may offer more affordable options. |
| Research Mortgage Options | Compare conventional, FHA, VA, and USDA loans to find the best fit for your needs. |
These strategies ensure you’re prepared to buy whenever you find a suitable opportunity, regardless of price trends.
8. Conclusion
So, when will home prices go down? While certain factors could slow price growth, a major drop in home prices is unlikely without a significant economic event. Economic indicators, supply-demand imbalances, and regional trends suggest that while prices may stabilize or rise more slowly, widespread price reductions may not be on the horizon.

